Portable Power Stations – Frequently Asked Questions
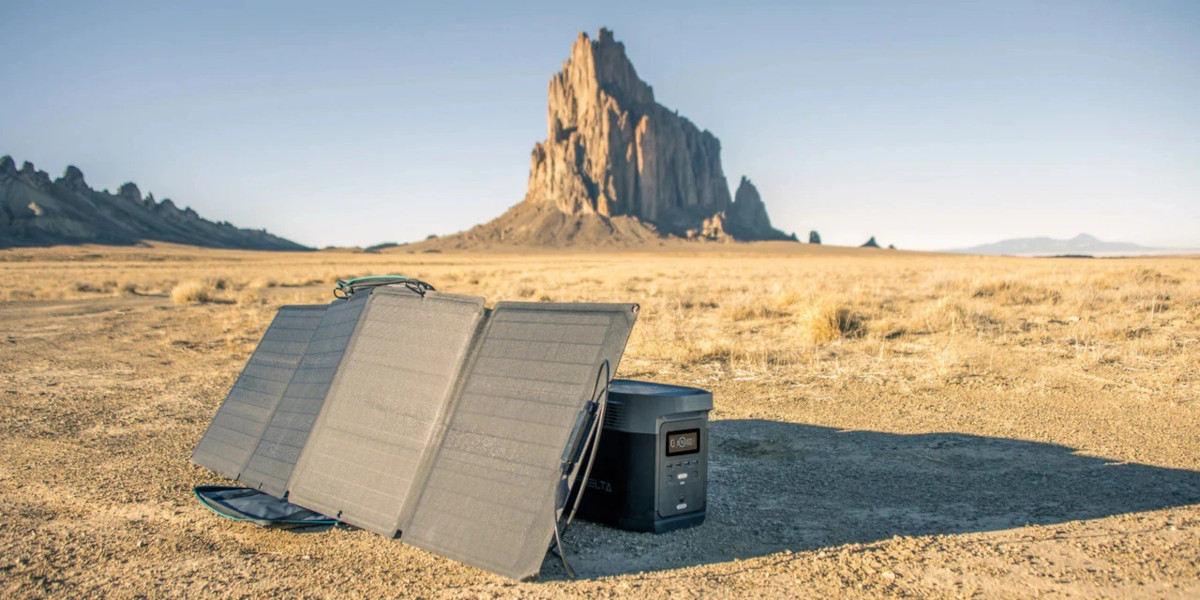

In some ways, Portable Power Stations are a lot like portable generators. They are portable; you can take them anywhere. Both require a source of energy. Most importantly, they provide power where you need it, even when there’s no other source of electricity. You can use them for backup power during an outage, power up your RV—including the air conditioner, take them camping or tailgating to power lights, fans, entertainment, or use them to power tools and charge your electronics.
Portable Power Stations do all these things without making a sound.
 What is a Portable Power Station?
What is a Portable Power Station?
Simply put, a portable power station is the combination of a rechargeable battery and a DC-AC inverter. Charge the battery and use it to power virtually anything that requires power—whether it requires DC or AC—provided it is within the capacity rating of the power station.
In this sense, a portable power station is an energy storage device. Depending on the battery capacity, it might store a few hundred to several thousand watt-hours of energy. The battery capacity and the rate at which it can safely discharge are what limit the rated output power.
It’s important to understand the difference between the rated output capacity and the storage capacity.
- Storage Capacity: Rated in Watt-Hours (Wh) or Kilowatt-Hours(kWh). For example, a 100Wh storage capacity means the power station’s battery can store enough energy to output 100 watts continuously for 1 hour, 50 Watts for 2 hours, or 25 watts for 4 hours.
- Rated Output: Rated in Watts (W) or Kilowatts (kW). A rating of 100 running watts means the power station supplies up to 100 watts of power to operate any device. Most also have a starting watts or maximum watts rating required for starting a motor that is 1.5–2 times the rated output. This becomes important to know if you plan to operate an appliance with a motor, like a refrigerator.
Understanding Running Watts vs Starting Watts
The cost of recharging the power station is minimal, but it takes time. A power station requires a little more than the unused storage capacity to recharge. For example, a 1000Wh power station at 20% charge can hold an additional 800Wh of energy. Plug it into an outlet, and it will use a little more than 800Wh of electricity to charge. If the electricity costs $0.15 for each kWh used, then charging the power station costs less than 15 cents.
 How Does a Portable Power Station Work?
How Does a Portable Power Station Work?
A power station converts energy stored in a battery to electricity. Charge the power station battery, plug in your device, and it has power. As the device operates, the energy stored in the battery depletes at the same rate as the device uses it. A 100Wh power station charging a cell phone at 25 watts will run out of power in 4 hours (4 x 25W=100W).
Some power stations allow you to swap batteries. Use one battery while the other battery is charging. This has the added benefit of extending the life of the power station because batteries have a limited number of charges over time.
Extra batteries in other models can extend storage capacity well beyond the single battery. In one example, a power station for an RV with 2000Wh capacity with a single battery extends the power to 8000Wh with the addition of 3 additional batteries.
Additional batteries increase the output capacity. A 1000-Watt Output becomes 2000 Watts with the addition of a second battery.
5 Ways to Keep the Power On
 How Long Does a Portable Power Station Last?
How Long Does a Portable Power Station Last?
Energy capacity—the amount of run time you get before recharging.
Battery chemistry—how many times you can recharge the battery.
Energy Capacity
Terms to know:
- Energy capacity—the amount of run time you get before recharging.
- Battery chemistry—how many times you can recharge the battery.
Energy Capacity
The rated watts and the energy storage capacity can be confusing. You might see a power station advertised as a 1000-watt power station, meaning it can output 1000 watts. If it has a battery capacity of 2000 watt-hours, the power station will last 2 hours at 1000 watts, or 4 hours at 500 watts, 8 hours at 250 watts, etc. Just divide the capacity by the total load you intend to put on it, and you can determine how long it will last for that particular load.
Capacity (Wh) / Total Load (W) = Hours (h).
Capacity = 2000Wh.
Total Load = 500W
2000 watt-hours / 500 watts = 4 hours run time.
Battery Chemistry
All batteries have a limited number of charge cycles. A charge cycle is one complete charge followed by a complete discharge.
The power station specifications should include a charge cycles rating. This is entirely dependent on the battery chemistry and the quality of the charge controller. Some Lithium-iron-phosphate batteries maintain 80% of their original charge capacity through 4000 or more charge cycles, while many Nickle-cadmium batteries have a lower rating of around 600-800 cycles.
The state of the battery charge when you store it is also important. Check the manufacturer's owner manual for best storage practices.
A power station could last many years before it needs replacement. With a 1000 charge cycle rating, you could do a complete charge/discharge cycle every day for 2 years 9 months before reaching 80% original capacity. That’s an unlikely scenario for most people, but it makes a good example of how long a portable power station lasts.
In practice, at one-two charge/discharge cycles per week, a portable power station with a 1000 charge cycle rating will last 10-20 years unless you’re doing a complete charge/discharge cycle every day as might be the case with off-grid homes. In that case, choose a power station with a 3000-5000 charge cycle rating.
 How to Charge a Portable Power Station?
How to Charge a Portable Power Station?
There are quite a few ways to charge a portable power station, from solar to grid to EV charging station.
Solar: Find the maximum solar input rating in your specifications. Connect solar panels up to the maximum input rating. Be sure to keep your solar panels pointed at the sun.
Grid: Just plug it into the wall outlet with the AC charging cord. The power station will charge at the maximum rate for AC charging.
USB: Depending on your cable and charger, the max power from USB-C is 240 watts, but many cables top out at 60W, some at 40W. There are 140W chargers and cables available. Check your power station specifications for maximum charging rates.
Auto, Van, RV: You can charge your power station while you drive. At less than 100 watts, it’s one of the slower ways to charge, but it’s good for topping off your battery on a road trip while you drive
EV: If your power station allows EV charging, the EV charger is usually the fastest method available. An electric vehicle charging station provides fast charging for high-capacity power stations and power station batteries.
Generator: If there’s no other source available, plug your power station into a generator outlet. The battery will charge at the same rate as the wall outlet.
Combined Charging: If your power station allows it, you can combine charging methods to charge faster. Combined charging capability varies—check your owner manual or specifications.
Solar Panels and Solar Panel Accessories
 What Is the Best Portable Power Station for CPAP?
What Is the Best Portable Power Station for CPAP?
Portable power stations let you take your CPAP places you normally wouldn’t take it. They also provide backup power during an outage so you can sleep easy.
At a minimum, you need enough storage capacity to run your machine for one complete night’s sleep. A regular CPAP can use up to 120 watts with a heated humidifier. A heated hose adds to the power draw.
If 1 night's sleep is 8 hours on a regular CPAP with a humidifier, then 120 Watts x 8 hours = 960 watt-hours of capacity. If you need 2 nights, turn off the humidifier and use a regular hose, and you can probably get 16 hours of running time. Or just increase the capacity to whatever you need.
Your machine’s documentation should give you the power requirements. Machines should also have a tag or printed information on the machine that provides the information.
The best portable power station for CPAP machines is one that gives you a full night of worry-free sleep using your machine.
 How To Use a Portable Power Station?
How To Use a Portable Power Station?
For simple everyday use, it’s easy. Charge your power station using the easiest or most convenient method available.
Turn it on, plug in your appliances, and they will have power. It’s that easy.
A few caveats:
- Don’t exceed the maximum rated watts.
- The more you plug in, the faster you will use the battery.
- Only charge while driving. Idling will allow it to draw from the car’s battery instead of the alternator. It’s okay for a few minutes while you fill the gas tank, but don’t charge while parked for long periods.
- Check the storage requirements and follow them.
- Don’t store the power station when it is fully or nearly depleted.
- If the battery is at less than 30% capacity, charge it up before using.
 How Big of a Portable Power Station Do I Need?
How Big of a Portable Power Station Do I Need?
It depends on your use.
Keep the refrigerator cold during a short outage: A few thousand watt-hours will get you through a half day or longer if you keep the door closed.
Tailgate party with television and slow cooker: Total load is 400 watts x 3-hour-long party = 1200 watts. Add another 300 watts so you don’t run it down to zero.
Camping weekend: Power a few strings of lights, a light in the tent, and a fan. You’ll enjoy the weekend with 500-1000 watts. Bonus: Bring along one or two 100-watt solar panels to charge during the day.
Weekend RV trip: Plan on rooftop solar to supplement power and an inverter generator to top off the batteries if necessary. With judicious A/C use, plan for 15,000 to 20,000kWh of battery capacity. A power station with an RV outlet will make it easier to connect.
 Can I Plug My RV into A Portable Power Station?
Can I Plug My RV into A Portable Power Station?
Yes, some portable power stations are RV ready with the standard TT-30R outlet for travel trailers and other RVs. The TT-30R is a 120-volt outlet capable of handling up to 30 amps of current.
Some systems are designed specifically for installation in an RV. Combined with rooftop solar panels, and you could stay off-grid for months or forever. Flexible solar panels can follow the contours of your roof. Ridged panels, either portable or installed, are another option. Start with your chosen system’s maximum solar charge capacity and use it to specify and build your solar array.
No matter where you live, there are times when the sun doesn’t shine or when your power use exceeds your capacity. A portable inverter generator can charge batteries or run your rooftop AC unit. Some power stations have the capability to start automatically and run a portable generator if the battery charge falls below a set point.
